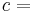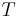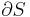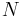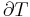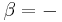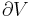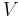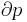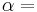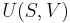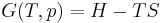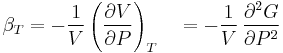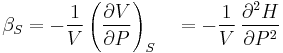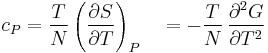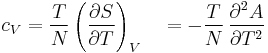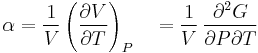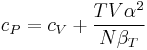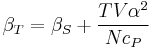Material properties (thermodynamics)
The thermodynamic properties of materials are intensive thermodynamic parameters which are specific to a given material. Each is directly related to a second order differential of a thermodynamic potential. Examples for a simple 1-component system are:
- Compressibility (or its inverse, the bulk modulus)
-
- Isothermal compressibility
- Adiabatic compressibility
- Specific heat (Note - the extensive analog is the heat capacity)
-
- Specific heat at constant pressure
- Specific heat at constant volume
- Coefficient of thermal expansion
where P is pressure, V is volume, T is temperature, S is entropy, and N is the number of particles.
For a single component system, only three second derivatives are needed in order to derive all others, and so only three material properties are needed to derive all others. For a single component system, the "standard" three parameters are the isothermal compressibility 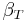 , the specific heat at constant pressure
, the specific heat at constant pressure 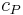 , and the coefficient of thermal expansion
, and the coefficient of thermal expansion 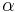 .
.
For example, the following equations are true:
The three "standard" properties are in fact the three possible second derivatives of the Gibbs free energy with respect to temperature and pressure.
Sources
The Dortmund Data Bank is a factual data bank for thermodynamic and thermophysical data.
See thermodynamic databases for pure substances.
References
Callen, Herbert B. (1985). Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatistics (2nd Ed. ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-86256-8.